Macs—and Apple products in general—tend to last a long time. It’s not unusual to see someone happily using an 8-year-old MacBook Pro. As much as it’s environmentally responsible to use electronics as long as possible, doing so may reduce your productivity or leave your business in a precarious situation if a hardware failure forces an upgrade at an inconvenient time.
Another factor to consider is whether or not you can get service and parts for your older device. It’s easy to assume that Apple will fix whatever you bring in, but unfortunately, that’s not the case. Apple has policies surrounding how long it guarantees to provide service and parts, which is reasonable. No one would expect Apple to repair a 128K Mac from 1984—many repair techs hadn’t even been born then.
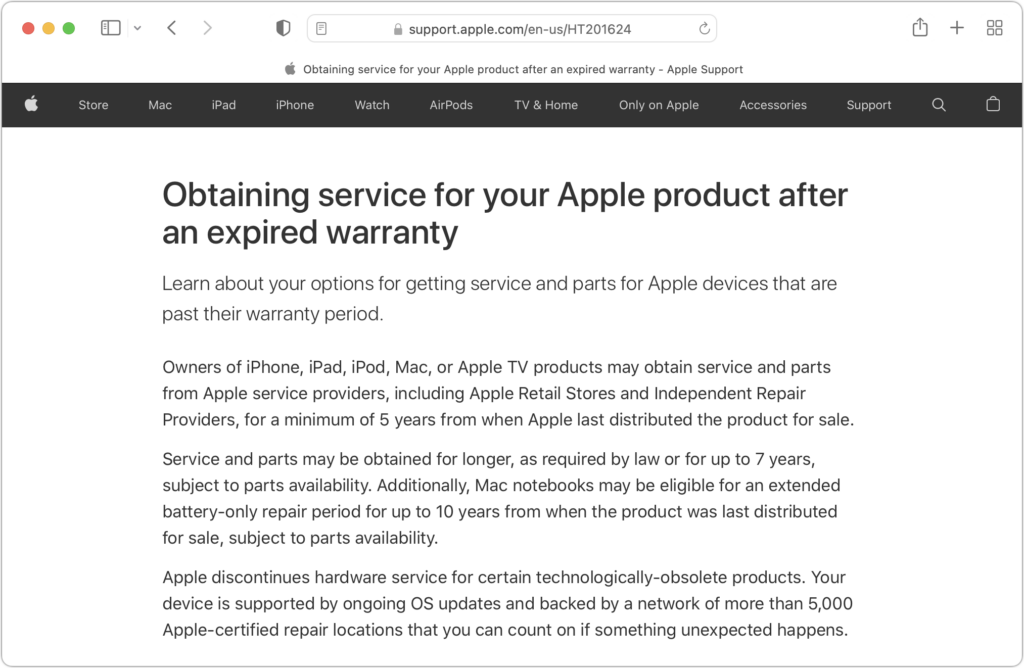
All Apple products fall into one of three categories: current, vintage, and obsolete. Current products, which Apple defines as those that were sold within the last 5 years, are eligible for service and parts from Apple, Apple Authorized Service Providers, and Independent Repair Providers. In other words, if you bought your Mac new within the last 5 years, you won’t have any problem getting Apple to fix it.
(Independent Repair Providers are firms that have signed up for Apple’s Independent Repair Provider Program to provide out-of-warranty iPhone and Mac repairs using Apple-provided parts, tools, service guides, and diagnostics. Other repair shops can repair Apple products but may lack Apple certifications and have to source parts from other suppliers.)
Things get trickier with the other two categories:
- Vintage: Apple considers a product to be vintage when the company stopped selling it more than 5 and less than 7 years ago. During this 2-year window, Apple says that service and parts may be obtained, subject to parts availability.
- Obsolete: As you’d expect, a product is considered obsolete when Apple hasn’t sold it for more than 7 years. Apple will not service obsolete products, and service providers cannot order parts for them.
There is one exception to these policies. Mac laptops may be eligible for an extended battery-only repair period for up to 10 years from when the product was last distributed for sale, subject to parts availability. That makes sense since a new battery may be all an old MacBook needs to keep working.
Apple maintains a page listing all vintage and obsolete products. To determine which Mac model you have, choose About This Mac from the Apple menu. For iPhones, iPads, and iPods, Apple provides pages explaining how to identify your model.
Apple’s policies surrounding vintage and obsolete products shouldn’t make a huge difference to most users. That’s because once a Mac hits 5 years old, it’s likely that upgrading to a new model will provide significant benefits. Many businesses prefer a 3-year replacement cycle because they’ve determined that’s the sweet spot where increasing support costs and lower performance make it worth selling the old Mac and buying a new one that’s faster and more reliable.
Of course, there’s nothing wrong with keeping a Mac longer if it meets your needs and you don’t mind spending more on support. At some point, though, products in the vintage and obsolete categories are living on borrowed time.
(Featured image by iStock.com/Soulmemoria)