We talked last month generally about real-time collaboration and why it’s so efficient and effective—see “Stop Mailing Files Around and Use Collaborative Apps.” Now we’re going to explain how to start collaborating in Apple’s iWork suite of apps: Pages, Numbers, and Keynote. Happily, the basics are similar in all three apps.
We’ll focus on the Mac versions here (make sure you have the latest updates!), but note that the iOS versions can participate as full-fledged collaboration citizens (Apple has more details). It’s even possible to use the iCloud versions of these apps for collaboration, but with some limitations (notably that Pages documents with tracked changes can only be viewed, not edited, in iCloud).
Invite Collaborators
Once you have a document you want to share, the first step is to invite your collaborators. Choose Share > Collaborate with Others, or click the Collaborate button in the toolbar.
The document must be stored in iCloud Drive (or the Box file sharing service), and the iWork apps will automatically move the file there if need be. To find the file later, choose Go > iCloud Drive in the Finder and look in the folder associated with the app you’re using.
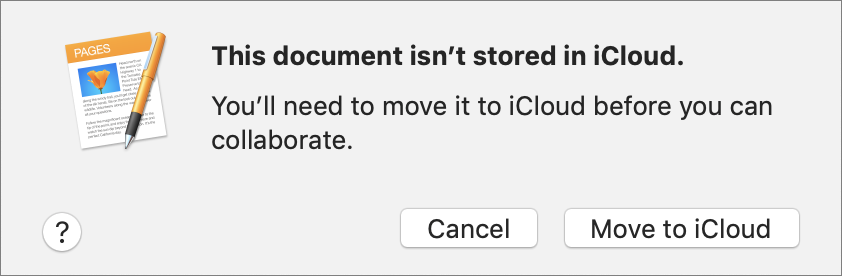
Next, the app displays the Add People dialog, where you can choose with whom you’re going to share the document, how to send the invitation, and what permissions to set.
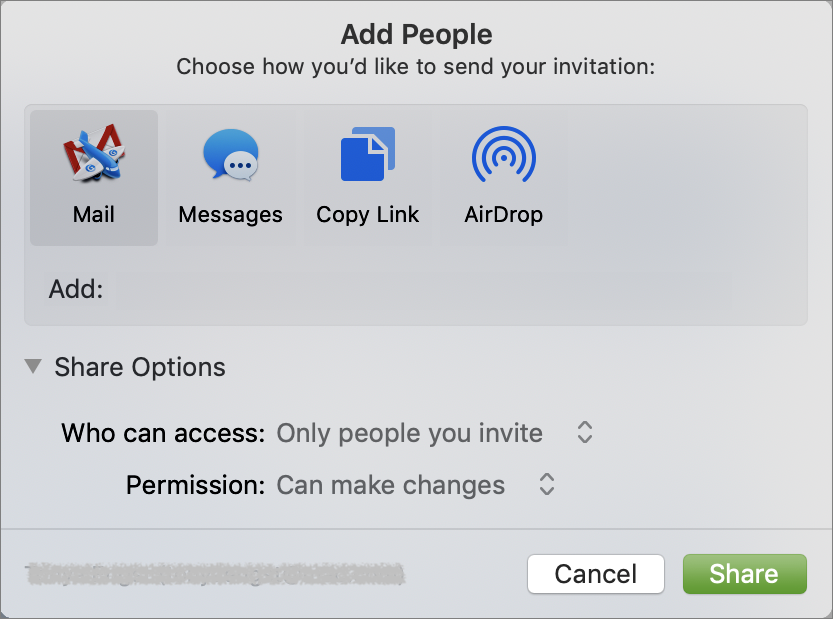
The Share Options are important. First, you can limit access to “Only people you invite” or “Anyone with the link.” With the former, the invitees must have iCloud accounts and be signed in. With the latter, you can share with anyone, even if they don’t use Apple devices.
Second, with the Permission menu, you can let collaborators make changes, or if you want them just to see the document, you can restrict them to View Only.
When you’re done, click Share to send the iCloud link via the specified channel (or copy it to the clipboard for sending in whatever way you prefer).
Accept an Invitation
When the recipient clicks the link or clicks Accept in a sharing notification, they get a dialog asking to open the document and telling them where it’s stored, in case they don’t want to work on it right away.
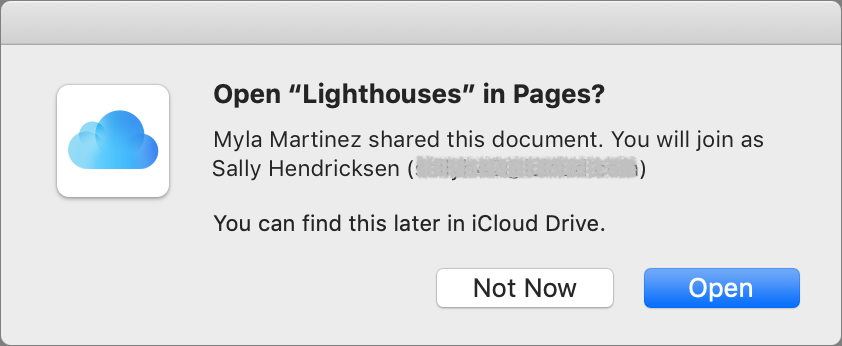
When they open the document, it will look and feel exactly like a normal document in Pages, Numbers, or Keynote.
For someone who isn’t an Apple user, clicking the iCloud URL will open the document in the Web version of the appropriate app on iCloud.com. They’ll need to enter a name to identify them in the document, after which they can work in the Web app.
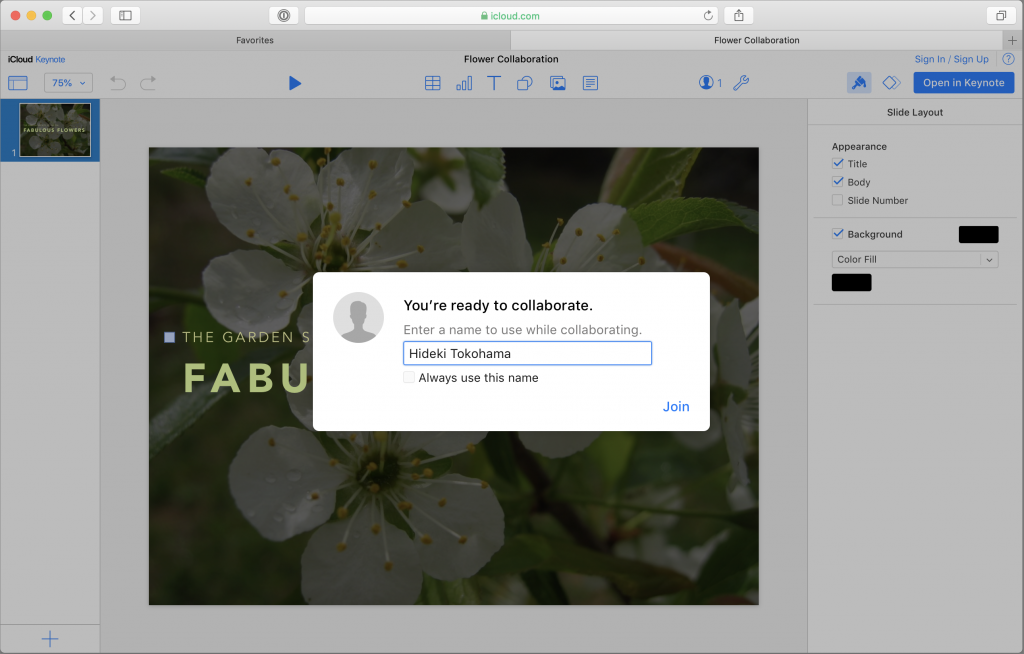
Add and Change Data
For the most part, you can do anything in a shared document that you can do with a normal document. There a few general limitations, such as managing styles and working with media files over 50 MB, plus some app-specific restrictions, such as working with tables of contents in Pages, transposing tables in Numbers, and changing themes in Keynote. Apple has a full list.
While you’re working, you can see who else is in the document at the same time by clicking the Collaborate button and looking for a colored dot next to a person’s name.
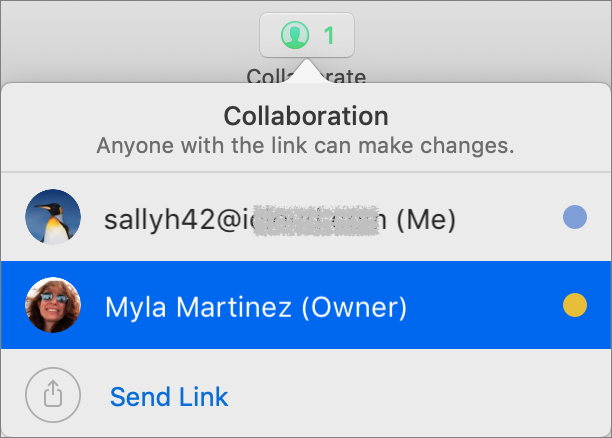
You’ll see color-coded cursors, text, and object selections as other people work, but if that’s distracting, choose View > Hide Collaboration Activity.
It can be hard to be work in a document while seeing someone else making changes, so don’t be shy about hiding collaboration activity. Or, if you are actively working with someone on a particular part of the document, consider doing so while you can talk in person or on the phone.
Add Comments
Commenting is the big win for collaboration with remote colleagues—it can save a vast amount of time to discuss a particular aspect of a document in context. To add a comment, select some text or an object, and then choose Insert > Comment or click the Comment button on the toolbar. (The controls look a bit different in iOS; Apple explains the differences.)
Comments appear as color-coded selections, boxes, or in the case of Numbers, corner triangles in cells. If they’re in the way, you can hide them by choosing View > Comments > Hide Comments. Other commands in View > Comments let you easily navigate to next and previous comments so you don’t have to find them visually.

Other collaborators can click Reply to continue the conversation right within that comment. You can edit one of your comments at any time by clicking to the right of the timestamp and choosing Edit Comment (or Edit Reply). Once the discussion has been resolved, either the person who started the comment thread or the document owner can delete the comment thread by clicking Delete.
Track Changes
Tracking who made what changes to a document is available only in Pages, and it’s hugely helpful when you need editing. Only the document owner can enable the feature by choosing Edit > Track Changes, but once that’s done, the change tracking toolbar appears above the document with controls for navigating between comments and changes, buttons for accepting or rejecting changes, and a button for pausing change tracking. A pop-up menu at the right side lets you configure whether you want to see all changes, changes other than deletions (which is generally the best setting), or what the document will look like in the end. A left-hand sidebar lists all comments and changes—show it by choosing View > Show Comments & Changes Pane.
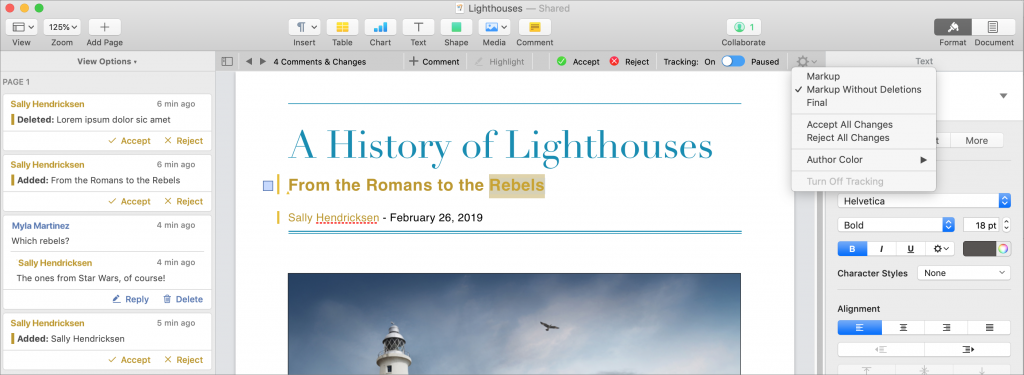
Anyone with edit access can accept or reject any particular change by clicking Accept or Reject in the Comments & Changes pane; you can also use the buttons in the change tracking toolbar to navigate from change to change, accepting and rejecting as you go. If there’s no need to deal with each change individually, use the pop-up menu’s commands to accept or reject all changes.
Needless to say, you can work on shared documents only when you’re online when you’re using the Mac or iOS version of an iWork app (if you try to edit while offline, the app will only let you edit a copy that is no longer shared). With any iCloud.com documents that you already have open, however, you can work offline, but your changes won’t appear to others until you reconnect.
When you’re done collaborating on a document, click the Collaborate button in the toolbar and then Stop Sharing (below left). Doing so immediately prevents others from making more changes and deletes the document from iCloud Drive on their devices (below right).

Simultaneous collaboration is wonderful when you’re working intensely with other people to develop a presentation, brainstorm budget estimates, or wordsmith a mission statement. In such situations, you’ll want to be able to talk at the same time. But for other sorts of projects, it’s also useful to allow people to collaborate when it’s convenient for them—the important thing is that everyone is working in the same document and can see each other’s changes and comments. If you rely on Apple’s iWork app for word processing, spreadsheets, or presentations, give their collaboration features a try!







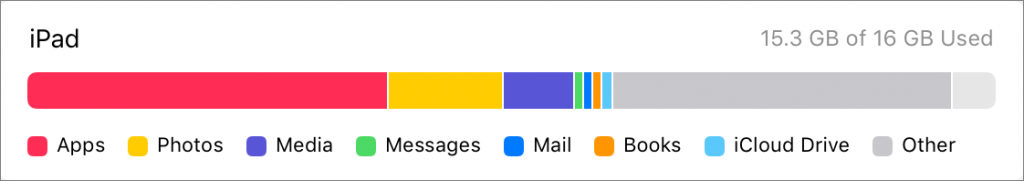
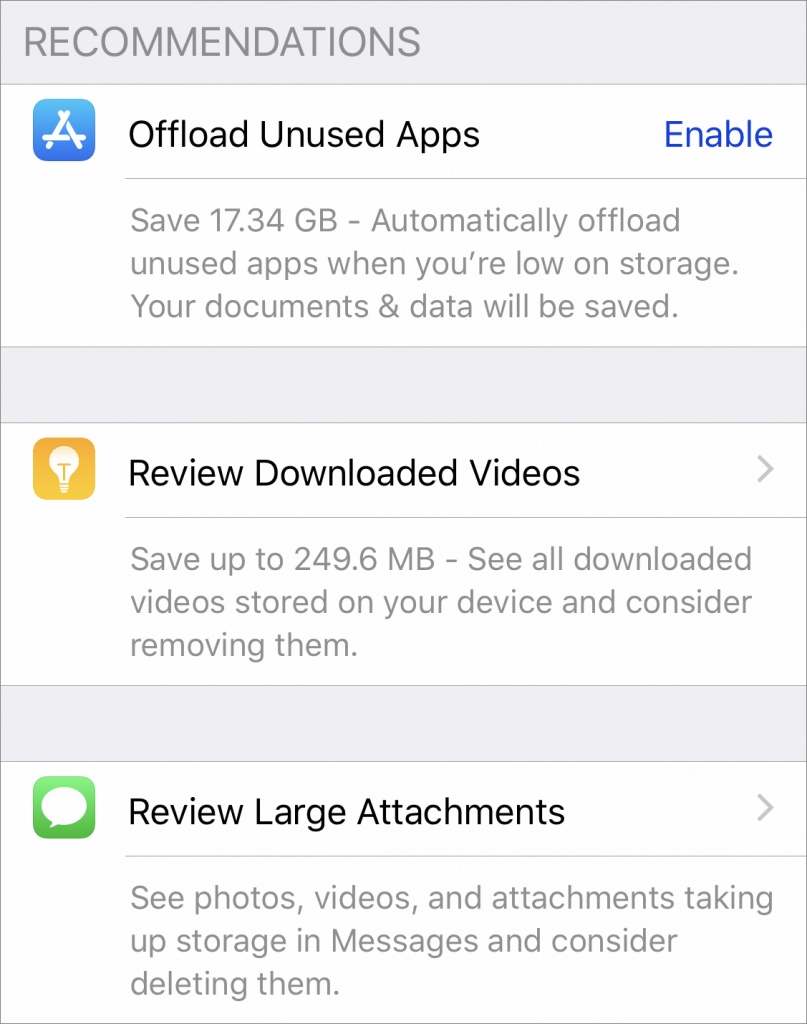
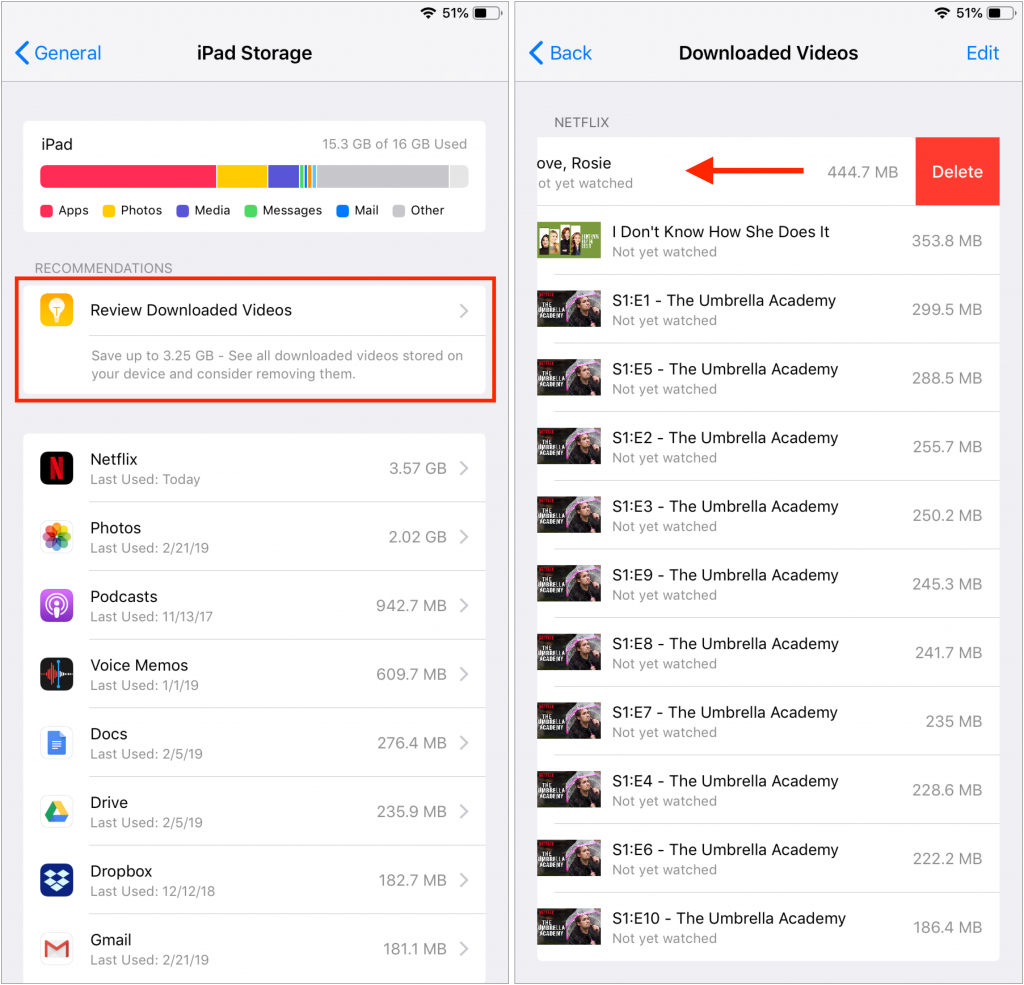
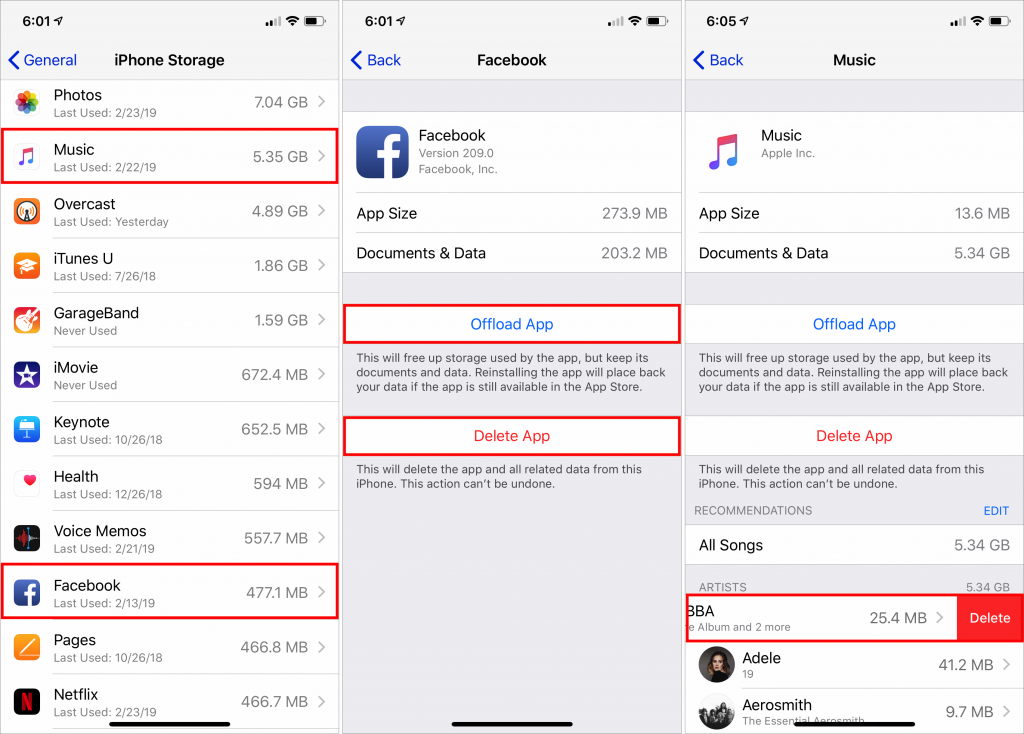
 Offload Unused Apps: This choice is particularly helpful if you download a lot of apps that you later stop using. Enable it, and iOS automatically recovers space from unused apps when you’re low on storage. Each of these apps remains on your Home screen with a little cloud icon next to it, and when you next tap the app to open it, iOS re-downloads the app from the App Store. You won’t lose any documents, data, or settings associated with an offloaded app.
Offload Unused Apps: This choice is particularly helpful if you download a lot of apps that you later stop using. Enable it, and iOS automatically recovers space from unused apps when you’re low on storage. Each of these apps remains on your Home screen with a little cloud icon next to it, and when you next tap the app to open it, iOS re-downloads the app from the App Store. You won’t lose any documents, data, or settings associated with an offloaded app.