Apple’s Messages app for iOS and macOS generally works well, but when it doesn’t, figuring out what’s wrong and how to fix it can take some doing. Here are a few of the most common solutions we’ve come across for problems with sending and receiving messages.
Help Android-switcher friends turn off iMessage
Do you have a friend who previously used an iPhone but later switched to an Android phone? People like that can confuse your copy of Messages, which doesn’t know if it should send to them via iMessage (no) or SMS (yes). If you text with someone in this situation, get them to deregister from iMessage.
Check device connectivity
If messages aren’t flowing when you think they should be, the first “is it plugged in?” thing to check is connectivity. Make sure that your iPhone has at least cellular service (for SMS) and cellular data (for iMessage) and that your iOS device isn’t in Airplane mode. In the case of a Mac, make sure it’s connected to your network.
Relaunch the Messages app
Force-quitting in iOS isn’t something you should do willy-nilly, since it slows down your device and hurts battery life, but it’s worth trying if Messages isn’t sending or receiving messages correctly. Double-press the Home button on Touch ID devices or swipe up and to the right from the bottom of the screen on Face ID devices, then swipe up on the Messages app thumbnail to force-quit it. On the Mac, just quit and relaunch Messages.
Toggle iMessage off and back on
Here’s an easy one. In iOS, go to Settings > Messages and turn the iMessage switch at the top off and back on. iMessage may take a minute or two to reactivate. On the Mac, go to Messages > Preferences > iMessage > Settings, uncheck Enable This Account, and then log in again.
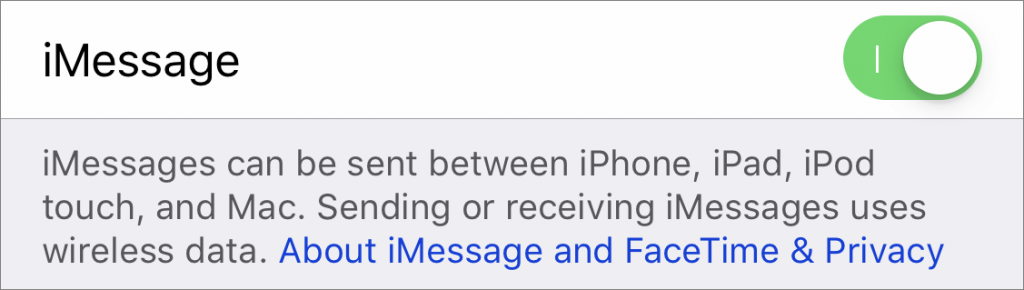
Toggle Messages in iCloud off and back on
With the new Messages in iCloud feature, Apple syncs conversations through your iCloud account. If messages from one device aren’t showing up properly on another device, in iOS, go to Settings > Your Name > iCloud and turn Messages off and back on. On the Mac, go to Messages > Preferences > iMessage > Settings and uncheck and recheck Enable Messages in iCloud.
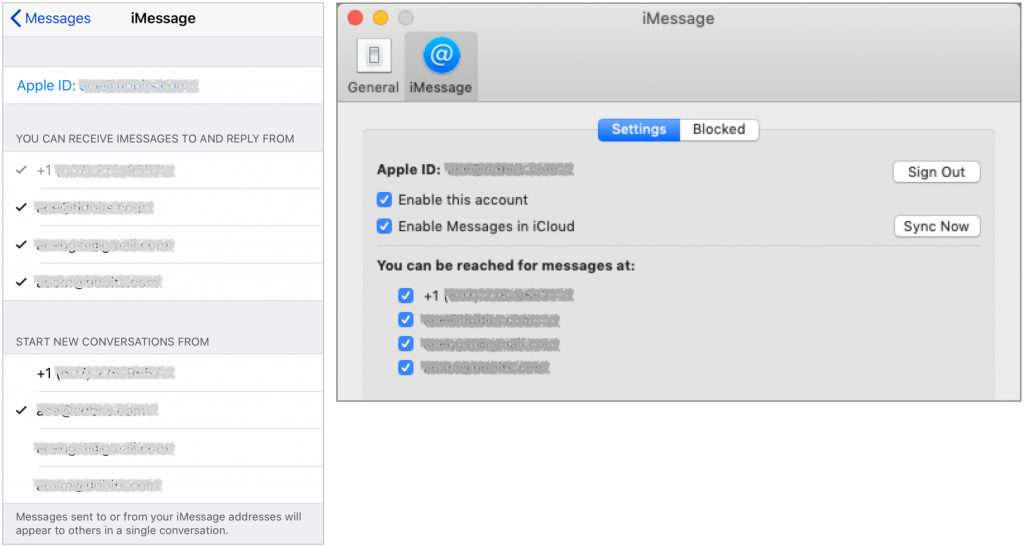
Verify your phone number and email addresses are correct in Messages settings
SMS relies on a phone number, and you can be contacted via iMessage via a phone number or email address. Make sure you can be reached at all the appropriate ones. In iOS, go to Settings > Messages > Send & Receive to check. On the Mac, look in Message > Preferences > iMessage > Settings.
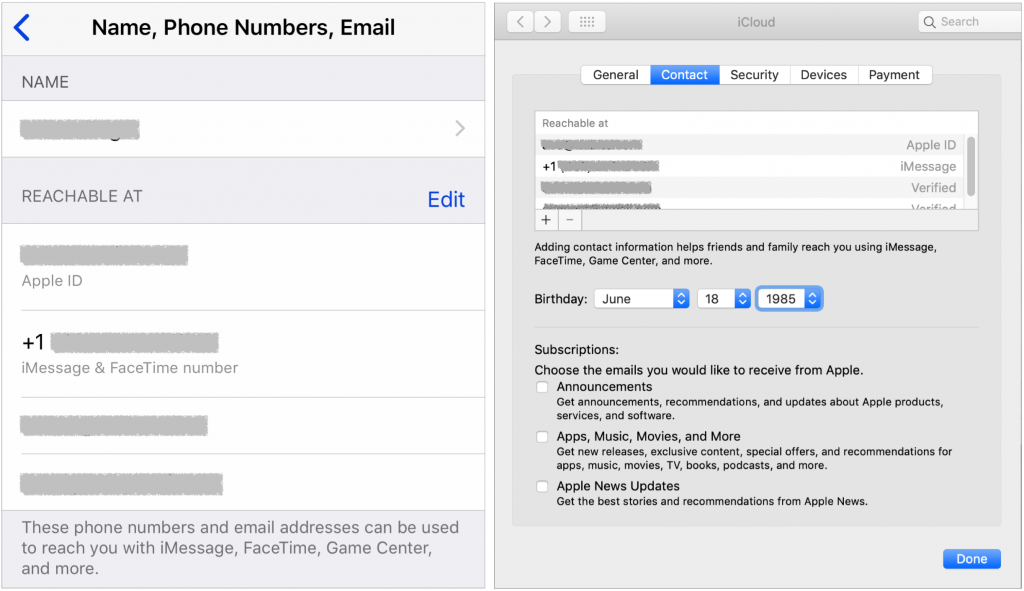
If they’re not right, fix them in iOS in Settings > Passwords & Accounts > iCloud > Your Name > Contact Information, by tapping Edit in the Reachable At section. On the Mac, you add these addresses with the plus button in System Preferences > iCloud > Account Details > Contact.
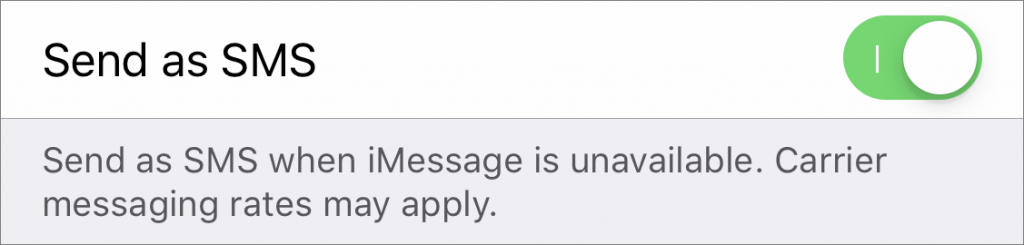
Verify that SMS fallback is enabled
When you’re in an area with sketchy cell service, there may not be enough of a data connection for iMessage to work. In such a situation, SMS text messages are more likely to get through, but Messages will try to send to iMessage users via SMS only if you turn on Send as SMS in Settings > Messages.
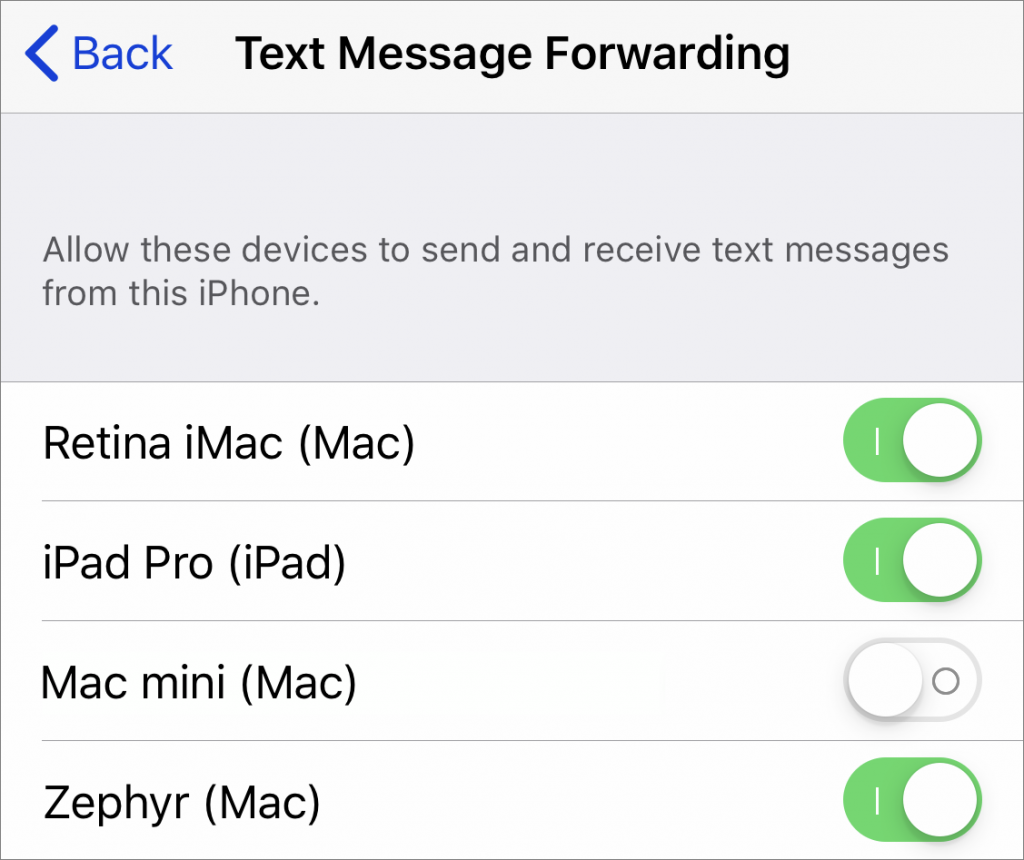
Check text message forwarding settings
If you’re receiving SMS messages on your iPhone but not any of your other devices, make sure Text Message Forwarding is enabled for the relevant devices (they need to be signed in to the same iCloud account). On your iPhone, look in Settings > Messages > Text Message Forwarding.
When in doubt, restart
Restarting can resolve all manner of problems, so it’s always worth a try if all the settings and accounts are correct. On the Mac, of course, just choose Apple > Restart. For iOS devices with Touch ID, press and hold the top button until the Slide to Power Off slider appears. For those with Face ID, press and hold the side (iPhone) or top (iPad) button and one of the volume buttons until the slider appears.
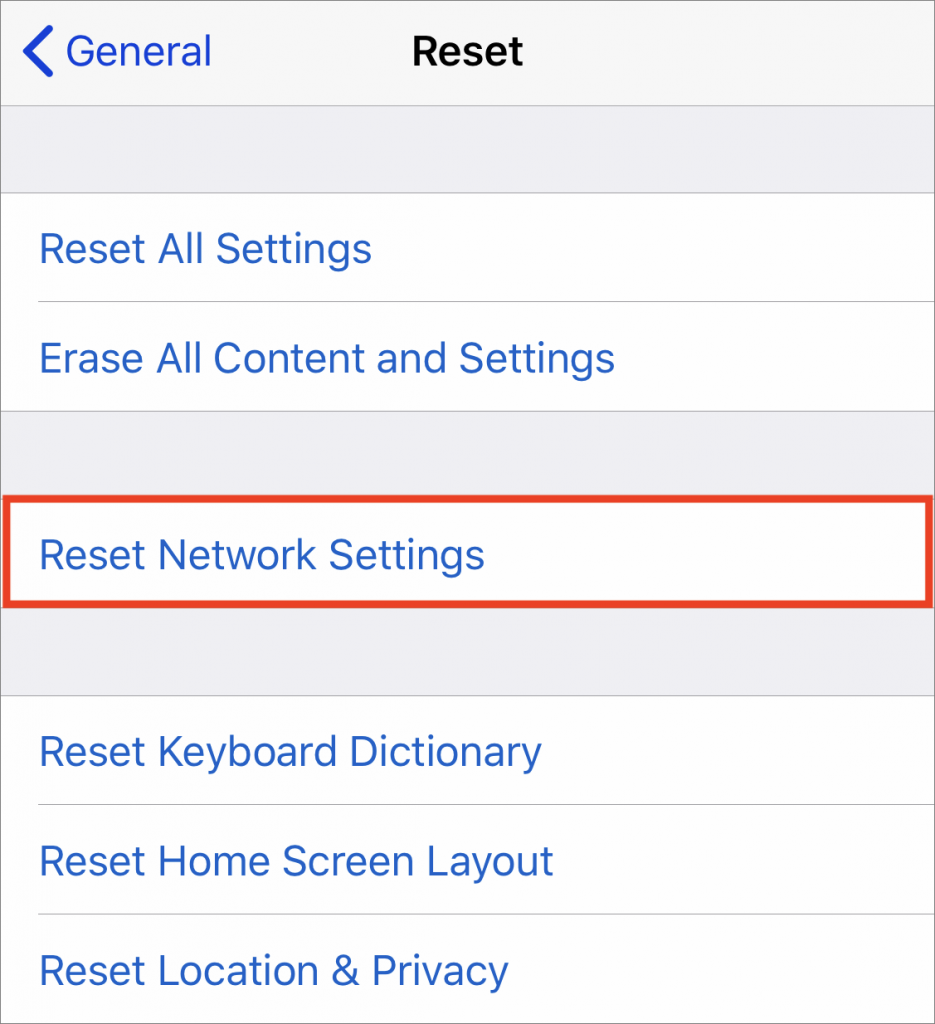
Reset network settings in iOS
Finally, the most voodoo of the fixes we’ve seen work is to reset network settings in iOS. You don’t want to start with this option because doing so also resets Wi-Fi networks and passwords, cellular settings, and VPN settings. But if all else fails, go to Settings > General > Reset > Reset Network Settings.
If none of these techniques fix your problem, let us know and we’ll see what we can do to help!