When it comes to upgrading to a new version of macOS, we err on the side of caution, at least in our recommendations. (We often install even beta releases on secondary machines for testing purposes.) Upgrading is easy, but if you upgrade too soon, the new version of macOS could render favorite apps inoperable, create workflow interruptions, and have other negative consequences. On the other hand, waiting too long can cause problems—it’s important so you can stay in sight of the cutting edge for security reasons and take advantage of Apple’s advances. Upgrading is not an if question; it’s a when question.
That “when” could be now. There’s no reason you must upgrade to macOS 12 Monterey right away, but if you want to, you should now be able to do so without undue interruptions. Monterey has been quite stable and has needed only two updates since its initial release in October 2021. The macOS 12.1 feature release in December 2021 added support for SharePlay, the Apple Music Voice Plan, Memories improvements in Photos, and Legacy Contacts, along with bug fixes and security updates. The macOS 12.2 maintenance release from January 2022 includes only unspecified bug fixes and some security updates. The upcoming macOS 12.3 will add the long-promised Universal Control feature for controlling multiple Macs and iPads from one keyboard and mouse. After that, Monterey should be feature-complete and will likely receive only bug fixes and security updates.
You can continue to delay as long as you’re running macOS 10.15 Catalina or macOS 11 Big Sur and are staying up to date with Apple’s security updates. Earlier versions of macOS no longer receive security fixes, rendering them more vulnerable to attack. Reasons to delay further include:
-
- You’re too busy. The upgrade process will take a few hours, and it may take additional time to configure everything properly afterward. When you are ready to upgrade, aim for when a little downtime will be convenient.
- You’re using incompatible software. The jump from Catalina or Big Sur to Monterey isn’t a big one, so most modern apps should have been updated to ensure compatibility with Monterey by now. But if you’re still running macOS 10.14 Mojave or earlier with 32-bit apps, you’ll lose access to them if you upgrade. (That happened first with Catalina.) With Mojave no longer receiving security updates, you need to find replacements for those apps and upgrade soon.
- You need consistent versions for workflow reasons. We’re unaware of any major issues here, but it’s not inconceivable that a coworker could be stuck on an older version of macOS and thus older versions of shared productivity apps. If your upgrade would force you to update those apps and introduce compatibility issues when collaborating with that coworker, you may have to wait until your coworker can upgrade as well.
Monterey won’t upend your experience of using a Mac, but it has numerous welcome features, both large and small. Apple radically improved FaceTime, introduced the Shortcuts app from iOS, added privacy enhancements like iCloud Private Relay and Hide My Email, enables you to copy text from images with Live Text, provides screen sharing in FaceTime calls, lets you always display the menu bar in full-screen mode, and much more. Perhaps even more important, Monterey shares numerous features with Apple’s other operating systems: iOS 15, iPadOS 15, watchOS 8, and tvOS 15. To take full advantage of those features across all your Apple devices, your Mac must be running Monterey.
Before You Upgrade
Once you’ve decided to upgrade to Monterey, you have three main tasks:
- Update apps: Make sure all your apps are as up-to-date as possible. If you regularly put off updates, now’s the time to let them complete so you have Monterey-compatible versions.
- Clear space: Monterey needs about 36 GB of free space to upgrade, and the Monterey installer itself is about 12 GB, so we recommend making sure you have at least 50 GB free. Don’t cut this close—you should always have at least 10–20% free space for virtual memory, cache files, and breathing room.
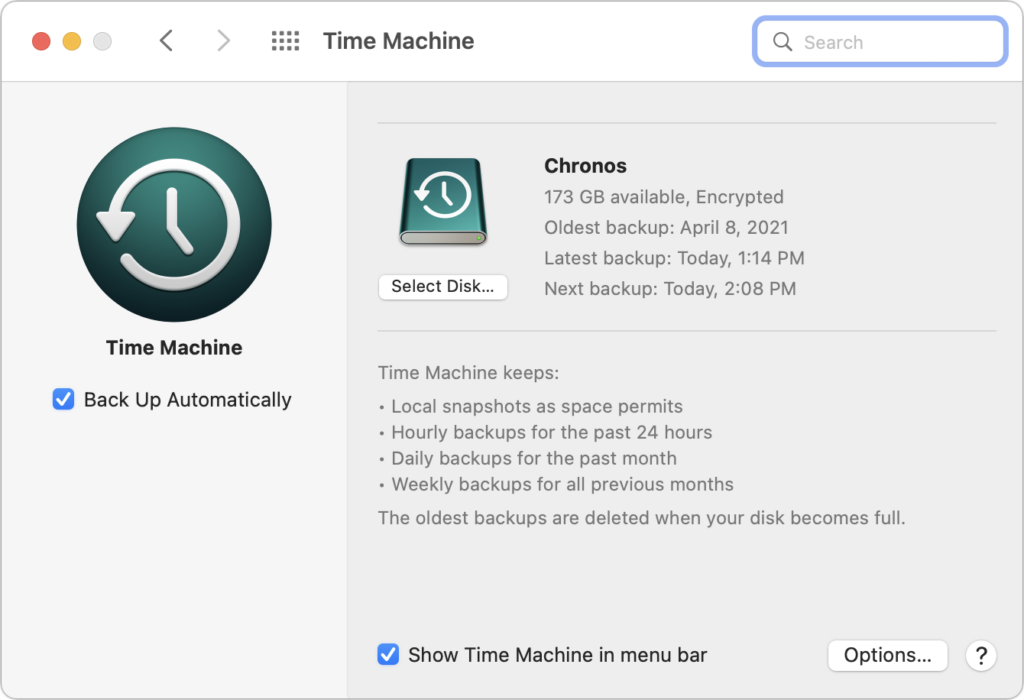
- Make a backup: Never, ever install a major upgrade to macOS without ensuring that you have at least one current backup first. In an ideal world, you’d have an updated Time Machine backup, a bootable duplicate, and an Internet backup. That way, if something goes wrong, you can easily restore.
Upgrading
After the above-listed tasks are complete, make sure you don’t need your Mac for a few hours. There’s no telling exactly how long the upgrade will take, so never start an upgrade if you need the Mac soon.
Initiating the upgrade is just a matter of opening System Preferences > Software Update, clicking the Upgrade Now button, and following the instructions. If you’d like more hand-holding, check out Joe Kissell’s ebook Take Control of Monterey.
After You Upgrade
Part of the reason to set aside plenty of time for your Monterey upgrade is that there are usually cleanup tasks afterward. We can’t predict precisely what you’ll run into, depending on what version of macOS you’re running now and what apps you use, but here are a few situations we’ve noticed in the past:
- macOS may need to update its authentication situation by asking for your Apple ID password, your Mac’s password, and if you have another Mac, its password too. Don’t worry that this is a security breach—it’s fine.
- Some apps may have to ask for permission to access your contacts and calendar even though you previously granted permission. Again, that’s fine and won’t happen again.
- If you use your Apple Watch to unlock your Mac and apps (and you should, it’s great!), you may need to re-enable that in System Preferences > Security & Privacy > General.
- If you use Gmail, Google Calendar, or other Google services, you may need to log in to your Google account again.
- Websites that usually remember your login state may require that you log in again. If you’re using a password manager like 1Password, that’s easy.
- You may have to re-enable text message forwarding to your Mac on your iPhone in Settings > Messages > Text Message Forwarding.
With all that housekeeping done, it’s time to check out all the new features in Monterey!
(Featured image by Apple)